ADENOID HYPERTROPHY , DK JHA,MD
Friday, August 1st, 2014INTRODUCTION:
Adenoid is an aggregation of lymphoid tissues located between nasal septum and posterior pharyngeal wall,also called nasopharyngeal tonsil.
It is separated from underlying structure by thick fibrous capsule.
There is only one adenoid in our body,so the term adenoids should not be used.
It forms a part of waldeyer’s ring which a defensive ring of our body.
It is situated at the external opening of pharynx and acts as first defence along with tonsils against external insult.
It induces the formation of secretory immunoglobulins.
It is present at birth but most active between the ages of 4-10 years and in some children may be most active between the ages of 6 months to 5 years. After puberty its immunological role is negligible.
It gets hypertrophied and become enlarged,due to internal and external insults and its increased size causes various troubles to the child.
Adenoid hypertrophy or enlarged adenoid is the most common cause of obstructive sleep apnea in children.
ETIOLOGY:
Infective causes include viruses which are the commonest cause of adenoid enlargement by causing adenoiditis.
Bacterial causes include both aerobics such as Streptococci and Haemophilus influezae and anaerobics such as Peptostreptococci,Prevotella and Fusobacterium.They are responsible for causing chronic adenoiditis and consequent adenoid enlargement.
The most common bacterium isolated from chronic adenoiditis is Haemophilus influenzae.
Among non infective causes ,most common cause of adenoid enlargement is allergic adenoiditis which is often recurrent.
In children with allergic rhinitis,the inflammatory or infected secretions sweep over adenoid regularly and causes its hypertrophy.
In children with gastroesophageal reflux disease ,there is regular contact of gastric contents with adenoid which causes chronic inflammation and hypertrophy.
CLINICAL FEATURES:
Day time symptoms are-
persistent mouth breathing due to nasal obstruction.
Foul smelling breath,due to mouth breathing,which bypasses the nasal filtering mechanism of bacteria.
Earache,due to hindrance of clearance by eustachian tube secondary to blockage by enlarged adenoid,which predisposes to recurrent otitis media.
Day time excessive sleepiness,difficulty in concentration,poor school performance.
Decreased appetite.
Hyponasal speech.
Hyposmia.
Early morning fatigue.
Child takes long time to finish meals,because of compulsion to take breath while swallowing.He or She has to withhold swallowing ,takes breath and then swallow.
Night time symptoms are-
Drooling of saliva through angles of mouth.
Snoring while sleeping which is loud.
Frequent arousals due to obnstructive sleep hypopnea and apnea.
Choking while sleeping,gasping while in sleep,restlessness while sleeping,frequent change in sleep position,sleep talking,night terror,abnomal sleep position.
Diaphoresis.
Somnabulism.
Nocturnal cough.
Nocturnal enuresis.
clinical signs:
Unlike tonsils,adenoid can not be seen on clinical examination.
It can be seen by mirror examination which is held back in the throat.
It is well visualized by flexible endoscopy.
Enlarged neck lymph nodes ,particularly jugulodiagastric may be an associated finding.
DIAGNOSIS:The investigation of choice is
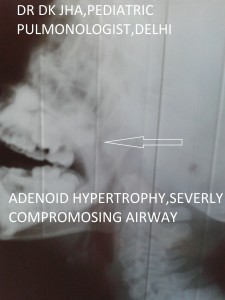
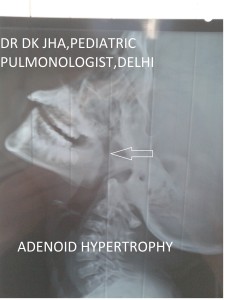
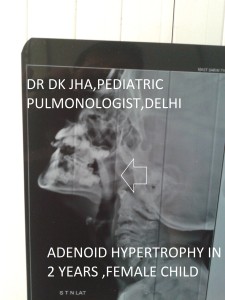
X-Ray soft tissue neck_lateral view
In these images middle part of the arrow is overlying adenoid while the point of arrow is showing indentation of the airway due to enlarged adenoid.
TREATMENT:
There are two nonsurgical modalities of treatment for adenoid hypertrophy apart from controlling infections if it is the cause.
INTRANASAL STEROIDS: Fluticasone,mometasone or budesonide nasal spray is quite effective in alleviating symptoms and also reduces the size of adenoids significantly. These should be given for a period of 12 to 24 weeks with a tapering dose. These are most effective in allergic individuals. Chances of recurrence is there after stopping therapy.
LEUKOTRIENE RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST(MONTELEUKAST): It is effective in alleviating symptoms and reducing the size of adenoids.
It should be given for a prolonged period,at least 3-6 months.
ATIBIOTICS: If there is evidence of bacterial infections ,causing adenoid enlargement , appropriate antibiotics should be given for 3 weeks.
GASTRO-ESOPHAGEAL REFLUX should be treated adequately if it suspected to be a cause.
ORAL STEROID-In acute conditions, with severe airway obstruction,prednisolone in the dose of 1-2 mg/kg/day should be given for 5 days to relieve the symptoms.
LONG TERM EFFECTS OF UNTREATED ADENOID HYPERTROPHY
Difficult to control asthma, if it is associated ,as commonly seen in allergic children.
Neurocognitive abormalities.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disordes.
Adenoid facies-elongation of the middle part face with retrognathia.
Growth retardation.
Diastolic hypertension.
Right ventricular hypertrophy.
pulmonary hypertension.
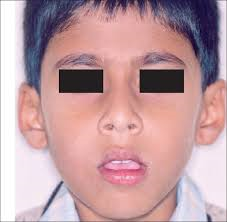 PICTURE SHOWING ADENOID FACIES
PICTURE SHOWING ADENOID FACIES
INDICATION FOR SURGICAL TREATMENT
Chronic nasal infections- chronic adenoiditis
Chronic sinus infections with failure to medical treatment
Recurrent otitis media including those with tympanostomy tube with recurrent otorrhoea
Recurrent otitis media with effusion
Craniofacial and occlusive developmental abnormality due to adenoid enlargement
Growth retardation
BIBLIGRAPHY
-
: Adherent biofilms in adenotonsillar diseases in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 134:20–232008 18209130
-
:Clinical indicators: tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy, adenotonsillectomy, 2000. (website)www.entlink.net/practice/products/indicators/tonsillectomy.htmlAccessed June 17, 2010
-
: Clinical practice guideline: tonsillectomy in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 144 (1 suppl):S1–S30 2011 21493257
-
: Growth and growth biomarker changes after adenotonsillectomy: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child. 94:83–91 2009 18684748
-
: Bacteriology of adenoids and tonsils in children with recurrent adenotonsillitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 110:844–8482001 11558761
-
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD006286. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006286.pub2.
Intranasal corticosteroids for nasal airway obstruction in children with moderate to severe adenoidal hypertrophy.
Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010 Jul;74(7):773-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.03.051. Epub 2010 Apr 28.Medical treatment of adenoid hypertrophy with “fluticasone propionate nasal drops”.
-
Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Apr;27(8):432-3, 439.
[Non-surgical treatment for adenoidal hypertrophy][Article in Chinese]
.